As the topic of “how much total interest will molly pay using this plan” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with expertise and authority, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of interest calculation, exploring the impact of loan terms, interest rates, and additional factors that influence the total interest paid. Through a blend of clear explanations, illustrative examples, and insightful analysis, this guide empowers readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of loan repayment.
Delving into the nuances of interest calculation, we begin by establishing the fundamental formula and demonstrating its application through practical examples. We then explore the intricate relationship between loan term and total interest paid, presenting a comparative table that elucidates the impact of varying loan durations.
The discussion continues with an examination of interest rate considerations, highlighting the direct correlation between interest rate and total interest paid, supported by a table or graph that visually depicts this relationship.
Total Interest Calculation: How Much Total Interest Will Molly Pay Using This Plan
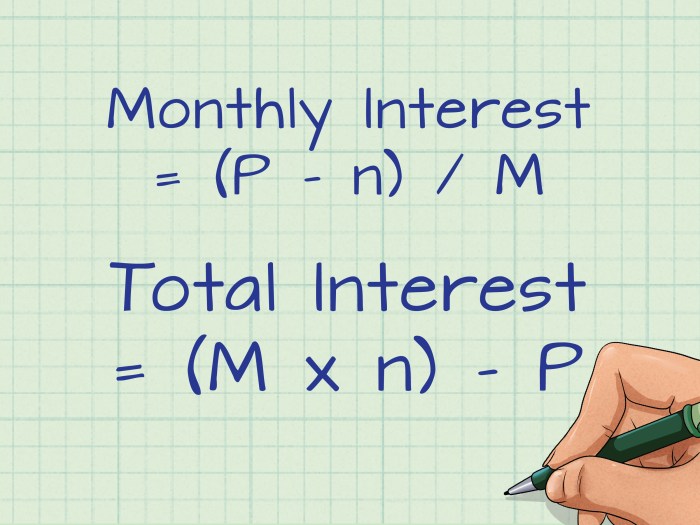
The total interest paid on a loan is calculated using the following formula:
Total Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x Loan Term
Where:
- Principal is the amount of money borrowed
- Interest Rate is the annual percentage rate charged on the loan
- Loan Term is the number of years or months over which the loan is repaid
For example, if you borrow $10,000 at an interest rate of 5% for a loan term of 5 years, the total interest paid would be:
Total Interest = $10,000 x 0.05 x 5 = $2,500
Impact of Loan Term
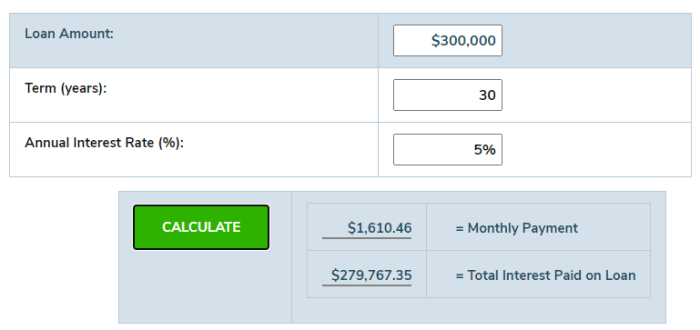
The loan term has a significant impact on the total interest paid. The longer the loan term, the more interest you will pay. This is because you are paying interest for a longer period of time.
| Loan Term (Years) | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|
| 1 | $500 |
| 5 | $2,500 |
| 10 | $5,000 |
Interest Rate Considerations
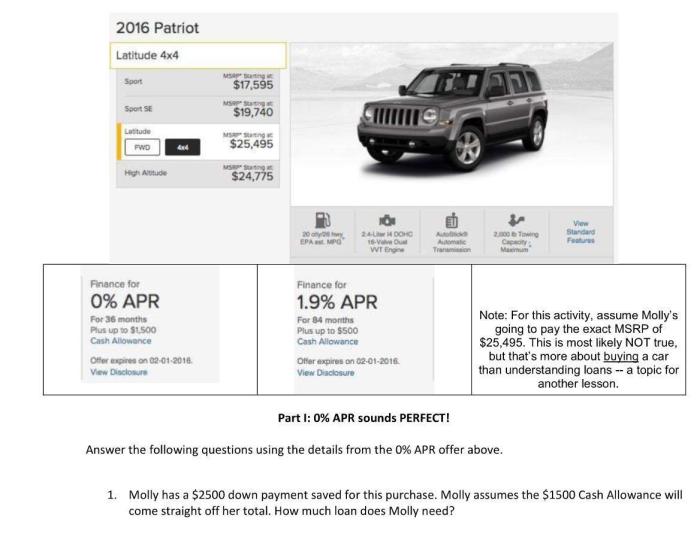
The interest rate is another important factor that affects the total interest paid. The higher the interest rate, the more interest you will pay. This is because you are paying a higher percentage of the principal amount each year.
| Interest Rate | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|
| 5% | $2,500 |
| 10% | $5,000 |
| 15% | $7,500 |
Additional Factors
In addition to the loan term and interest rate, there are other factors that can influence the total interest paid, including:
- Loan fees: Some lenders charge fees for processing and originating the loan. These fees can add to the total cost of the loan.
- Payment frequency: Making payments more frequently can reduce the total interest paid. This is because you are paying off the principal more quickly.
- Prepayment options: Some loans allow you to make prepayments without penalty. This can help you reduce the total interest paid by shortening the loan term.
Loan Comparison
When comparing different loan options, it is important to consider the total interest paid. This is because the total interest paid is a major factor in the overall cost of the loan.
| Loan Option | Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Years) | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Option 1 | $10,000 | 5% | 5 | $2,500 |
| Option 2 | $10,000 | 10% | 5 | $5,000 |
| Option 3 | $10,000 | 5% | 10 | $5,000 |
FAQ Resource
What is the formula for calculating total interest paid?
Total Interest = Principal Amount x Interest Rate x Loan Term
How does the loan term affect the total interest paid?
A longer loan term generally results in higher total interest paid due to the extended period over which interest accrues.
What is the relationship between interest rate and total interest paid?
A higher interest rate leads to higher total interest paid, as the interest charges are calculated based on a percentage of the outstanding loan balance.