Delving into the realm of chemistry, the empirical formula worksheet 1 answer key emerges as a pivotal tool, providing a comprehensive guide to deciphering the elemental makeup of compounds. This key unlocks a treasure trove of knowledge, empowering students to navigate the intricacies of chemical composition with precision and confidence.
Empirical formulas, the foundation of this worksheet, offer a simplified representation of a compound’s composition, revealing the relative proportions of its constituent elements. Armed with this knowledge, chemists can unravel the mysteries of molecular structures, predict chemical reactions, and gain invaluable insights into the behavior of matter.
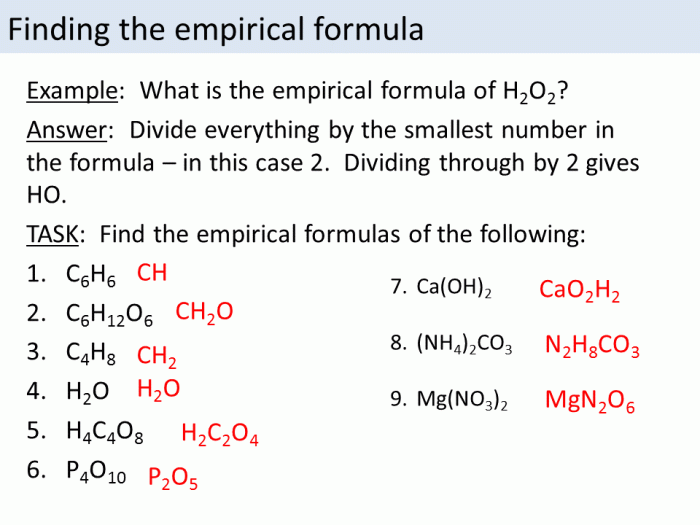
Empirical Formula Basics
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements present in a compound. It provides information about the relative proportions of different elements in a compound but does not specify the actual molecular structure or the arrangement of atoms within the molecule.
For example, the empirical formula for glucose is CH 2O, indicating that for every carbon atom, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. However, the molecular formula for glucose is C 6H 12O 6, which shows the actual number of atoms present in the molecule.
Empirical formulas are significant in chemistry because they provide a basic understanding of the elemental composition of a compound. They are used in various calculations, such as determining the molar mass, predicting chemical reactions, and understanding the stoichiometry of reactions.
Determining Empirical Formula

Determining the empirical formula of a compound involves several steps:
- Determine the mass of each element present in the compound using techniques such as combustion analysis or mass spectrometry.
- Convert the mass of each element to the number of moles using its molar mass.
- Find the simplest whole-number ratio of the moles of each element by dividing each mole value by the smallest mole value.
- Write the empirical formula using the whole-number ratios obtained in step 3.
Combustion analysis is a common technique used to determine the empirical formula of organic compounds. It involves burning a known mass of the compound in excess oxygen and measuring the masses of the products (carbon dioxide and water). From these measurements, the masses of carbon and hydrogen in the compound can be calculated.
Mass spectrometry is another technique that can be used to determine the empirical formula of a compound. It involves ionizing the compound and measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of the resulting ions. The empirical formula can be deduced from the relative abundances of the different ions.
Worksheet 1 Answer Key: Empirical Formula Worksheet 1 Answer Key

Problem 1:A compound is found to contain 40.0% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen, and 53.3% oxygen by mass. Determine its empirical formula.
Solution:
- Convert the percentages to grams:
- Carbon: 40.0 g
- Hydrogen: 6.7 g
- Oxygen: 53.3 g
- Convert the grams to moles:
- Carbon: 40.0 g / 12.01 g/mol = 3.33 mol
- Hydrogen: 6.7 g / 1.01 g/mol = 6.63 mol
- Oxygen: 53.3 g / 16.00 g/mol = 3.33 mol
- Find the simplest whole-number ratio:
- Carbon: 3.33 mol / 3.33 mol = 1
- Hydrogen: 6.63 mol / 3.33 mol = 2
- Oxygen: 3.33 mol / 3.33 mol = 1
- Empirical formula: CH 2O
Problem 2:A compound has a molar mass of 60.0 g/mol and contains 40.0% carbon and 60.0% oxygen by mass. Determine its molecular formula.
Solution:
- Determine the empirical formula:
- Carbon: 40.0 g / 12.01 g/mol = 3.33 mol
- Oxygen: 60.0 g / 16.00 g/mol = 3.75 mol
- Simplest whole-number ratio:
- Carbon: 3.33 mol / 3.33 mol = 1
- Oxygen: 3.75 mol / 3.33 mol = 1.125
- Empirical formula: CH 1.125O
- Multiply the empirical formula by a whole number to obtain the molecular formula:
- Molecular formula: C 2H 2O 2
Applications of Empirical Formulas
Empirical formulas have several practical applications in chemistry:
- Calculating molar mass:The molar mass of a compound can be calculated from its empirical formula by adding the atomic masses of all the elements present, multiplied by their respective subscripts.
- Stoichiometry:Empirical formulas are used in stoichiometry to balance chemical equations and determine the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- Predicting chemical reactions:Empirical formulas can provide insights into the possible chemical reactions that a compound may undergo based on the elements present and their relative proportions.
Additional Practice Problems
- A compound is found to contain 54.5% carbon, 9.1% hydrogen, and 36.4% oxygen by mass. Determine its empirical formula.
- A compound has a molar mass of 78.1 g/mol and contains 63.6% carbon, 13.6% hydrogen, and 22.8% oxygen by mass. Determine its molecular formula.
- Use the empirical formula of glucose (CH2O) to calculate its molar mass.
- Balance the following chemical equation using the empirical formulas of the reactants and products: CH 4+ O 2→ CO 2+ H 2O
Answer Key:
- Empirical formula: C4H 9O
- Molecular formula: C 6H 12O 6
- Molar mass: 30.03 g/mol
- Balanced equation: CH 4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
Further Exploration
- Empirical Formula – Wikipedia
- Determining Empirical Formula from Percent Composition – Khan Academy
- Empirical Formula Definition and Examples – ThoughtCo
Q&A
What is the significance of empirical formulas in chemistry?
Empirical formulas provide a simplified representation of a compound’s composition, revealing the relative proportions of its constituent elements. This information is crucial for understanding the structure, properties, and reactivity of compounds.
How is combustion analysis used to determine empirical formulas?
Combustion analysis involves burning a known mass of a compound in excess oxygen and measuring the masses of the resulting carbon dioxide and water. From these measurements, the empirical formula can be calculated.
What are some practical applications of empirical formulas?
Empirical formulas find numerous applications in chemistry, including calculating molar mass, determining the stoichiometry of reactions, and predicting the properties of compounds.




