Cacl2 + na2so4 balanced equation – The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between CaCl2 and Na2SO4, CaCl2 + Na2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2 NaCl, reveals the stoichiometry of the reaction and provides insights into the physical and chemical properties of the reactants and products.
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) undergo a double displacement reaction to form calcium sulfate (CaSO4) and sodium chloride (NaCl). This reaction finds applications in various industries, including water treatment, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
Chemical Equation: Cacl2 + Na2so4 Balanced Equation
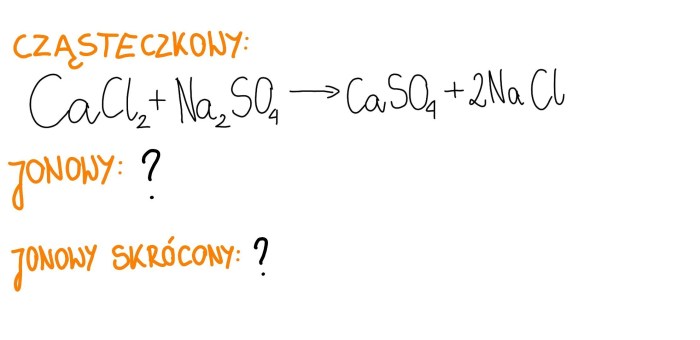
The chemical equation for the reaction between CaCl2 and Na2SO4 is:“`CaCl2 + Na2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2 NaCl“`This equation shows that one mole of calcium chloride (CaCl2) reacts with one mole of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) to produce one mole of calcium sulfate (CaSO4) and two moles of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
The stoichiometry of the reaction tells us the relative amounts of reactants and products that are involved in the reaction. In this case, the stoichiometry tells us that one mole of CaCl2 reacts with one mole of Na2SO4 to produce one mole of CaSO4 and two moles of NaCl.
This information is important because it allows us to calculate the amount of reactants and products that are needed or produced in the reaction.
Reactants
The reactants in the balanced chemical equation are calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4).
Physical and Chemical Properties of CaCl2
Calcium chloride is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It has a melting point of 772 °C and a boiling point of 1600 °C. Calcium chloride is a strong electrolyte and dissociates into calcium ions (Ca2+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in water.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Na2SO4
Sodium sulfate is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It has a melting point of 884 °C and a boiling point of 1404 °C. Sodium sulfate is a weak electrolyte and dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and sulfate ions (SO42-) in water.
Products
The chemical reaction between calcium chloride (CaCl 2) and sodium sulfate (Na 2SO 4) produces two products: calcium sulfate (CaSO 4) and sodium chloride (NaCl).
Physical and Chemical Properties
Calcium Sulfate (CaSO 4)* Physical properties:
White or colorless solid
Odorless
Crystalline structure
Chemical properties
Soluble in water
Forms a white precipitate when mixed with barium chloride solution
Decomposes upon heating
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)* Physical properties:
White or colorless solid
Odorless
Crystalline structure
High melting point
Chemical properties
Highly soluble in water
Forms a white precipitate when mixed with silver nitrate solution
Stable at room temperature
Solubility in Water
Both calcium sulfate and sodium chloride are soluble in water. Calcium sulfate has a low solubility in water, while sodium chloride has a high solubility. This difference in solubility is due to the different ionic radii of the calcium and sodium ions.
The calcium ion has a larger ionic radius than the sodium ion, which makes it more difficult for calcium sulfate to dissolve in water.
Reaction Conditions

The reaction between CaCl2 and Na2SO4 is a precipitation reaction that typically occurs in aqueous solutions. The reaction rate is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and concentration.
Effect of Temperature
Increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture generally increases the reaction rate. This is because higher temperatures provide more energy to the reactants, allowing them to overcome the activation energy barrier and react more quickly.
Effect of Pressure, Cacl2 + na2so4 balanced equation
Pressure has a negligible effect on the reaction rate of this precipitation reaction. This is because the reaction does not involve any gases, and therefore, changes in pressure do not significantly affect the reaction rate.
Effect of Concentration
The concentration of the reactants has a significant impact on the reaction rate. Increasing the concentration of either CaCl2 or Na2SO4 increases the likelihood of collisions between the reactants, leading to a faster reaction rate.
Applications
The reaction between calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) has several industrial applications, primarily due to the formation of calcium sulfate (CaSO4), which is a valuable product in various industries.
Calcium sulfate is widely used as a drying agent, a water softener, and in the production of cement, plaster, and other building materials.
In Desiccation Processes
Calcium sulfate is a highly effective desiccant, meaning it has a strong ability to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. This property makes it useful in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing, where it is used to remove moisture from products and packaging to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
In Water Softening
Calcium sulfate is also used in water softening processes. Hard water contains high levels of dissolved calcium and magnesium ions, which can cause scale buildup in pipes, appliances, and boilers. Calcium sulfate reacts with these ions to form insoluble calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which precipitates out of the water, effectively reducing its hardness.
In Construction
Calcium sulfate is a key ingredient in the production of cement and plaster. When mixed with water, calcium sulfate forms a paste that hardens over time, creating a strong and durable material. Cement is used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other structures, while plaster is used for interior wall finishes and decorative moldings.
User Queries
What is the molar ratio of CaCl2 to Na2SO4 in the balanced equation?
1:1
What are the physical properties of CaSO4?
White, crystalline solid with low solubility in water
What is the industrial application of the CaCl2 + Na2SO4 reaction?
Water softening and production of sodium chloride




